Short Questions
2. Kinematics
3. Dynamics – I
4. Dynamics – II
5. Pressure and Deformation in Solids
6. Work and Energy
7. Density and Temperature
8. Magnetism
9. Nature of Science and Physics
Physics 9 Short Questions and Answers – Chapters 1 to 9
Physics is a fundamental branch of science that helps us understand natural phenomena and the laws governing motion, energy, and forces. Below are important short questions and answers from Chapters 1 to 9 of 9th-grade physics.
Chapter 1: Physical Quantities and Measurement
Q1: What are physical quantities?
Answer: Physical quantities are measurable quantities that describe the laws of physics, such as length, mass, time, and temperature.
Q2: What is the SI system?
Answer: The International System of Units (SI) is a standard system of measurement used worldwide. It includes seven base units such as meter (m) for length and kilogram (kg) for mass.
Q3: Define significant figures.
Answer: Significant figures are the digits in a number that contribute to its precision, starting from the first non-zero digit.
Q4: What is meant by precision and accuracy?
Answer: Precision refers to the consistency of repeated measurements, while accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the actual value.
Chapter 2: Kinematics
Q5: Define displacement and differentiate it from distance.
Answer: Displacement is the shortest path between two points in a specific direction, whereas distance is the total length traveled without considering direction.
Q6: What is velocity?
Answer: Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time and includes direction.
Q7: What is uniform acceleration?
Answer: Uniform acceleration occurs when an object’s velocity changes at a constant rate over time.
Q8: State the three equations of motion.
Answer: The equations of motion are:
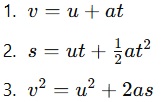
where u is the initial velocity, v is the final velocity, a is acceleration, ss is displacement, and t is time.
Chapter 3: Dynamics – I
Q9: Define force.
Answer: Force is a push or pull that causes an object to move, stop, or change direction.
Q10: State Newton’s first law of motion.
Answer: An object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
Q11: What is inertia?
Answer: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion.
Q12: Give an example of inertia in daily life.
Answer: When a car suddenly stops, passengers lurch forward due to their inertia.
Chapter 4: Dynamics – II
Q13: State Newton’s second law of motion.
Answer: The force acting on an object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration:
F=ma
Q14: What is momentum?
Answer: Momentum is the product of mass and velocity, given by:
p=mv
Q15: State Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Q16: What is the law of conservation of momentum?
Answer: The total momentum of an isolated system remains constant before and after a collision.
Chapter 5: Pressure and Deformation in Solids
Q17: Define pressure.
Answer: Pressure is the force exerted per unit area:
Q18: Why do sharp knives cut better than blunt knives?
Answer: Sharp knives have a smaller surface area, which increases pressure and makes cutting easier.
Q19: What is Pascal’s principle?
Answer: Pascal’s principle states that pressure applied to a fluid in a closed system is transmitted equally in all directions.
Q20: How does a hydraulic system work?
Answer: A hydraulic system uses Pascal’s principle to multiply force using incompressible fluids.
Chapter 6: Work and Energy
Q21: Define work.
Answer: Work is done when a force is applied to an object and causes displacement:
W=Fdcosθ
Q22: What is the unit of work?
Answer: The SI unit of work is the joule (J).
Q23: What is kinetic energy?
Answer: Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object, given by:
KE = 1/2 mv2
Q24: Define power.
Answer: Power is the rate at which work is done:
Chapter 7: Density and Temperature
Q25: Define density.
Answer: Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance:
Q26: What is the SI unit of density?
Answer: The SI unit of density is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).
Q27: What is absolute zero?
Answer: Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature (-273.15°C or 0K), where molecular motion stops.
Q28: How are Celsius and Kelvin related?
Answer: The temperature in Kelvin is given by:
K = C∘+273
Chapter 8: Magnetism
Q29: What is a magnet?
Answer: A magnet is an object that produces a magnetic field and attracts materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt.
Q30: What are the two types of magnets?
Answer:
-
Permanent Magnets: Retain their magnetism.
-
Temporary Magnets: Lose magnetism when the external magnetic field is removed.
Q31: State the law of magnetism.
Answer: Like poles repel, and opposite poles attract.
Q32: What are the properties of magnetic field lines?
Answer:
-
They originate from the north pole and end at the south pole.
-
They never intersect.
-
They are strongest at the poles.
Chapter 9: Nature of Science and Physics
Q33: What is physics?
Answer: Physics is the branch of science that deals with matter, energy, and their interactions.
Q34: What are the main branches of physics?
Answer: The main branches of physics include:
-
Mechanics
-
Thermodynamics
-
Electromagnetism
-
Optics
-
Nuclear Physics
Q35: Why is physics important in everyday life?
Answer: Physics is important because it helps in the development of technologies such as electricity, transportation, communication, and medical imaging.
Q36: What is the scientific method?
Answer: The scientific method is a systematic research approach that includes observation, hypothesis, experimentation, and conclusion.
Conclusion
These short questions and answers provide a quick and effective way to review key concepts in physics. By practicing these questions, students can strengthen their understanding and perform well in exams. 🚀 Happy learning!