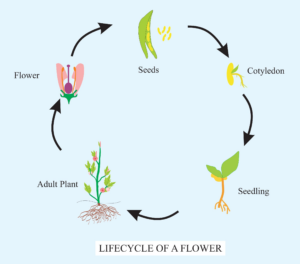
The life cycle of a flowering plant consists of several stages. Here’s an explanation of each stage:
1. Seed Stage:
- The cycle begins with a seed, which contains an embryo, stored food, and a protective coat.
2. Germination:
- Under favorable conditions (water, warmth, and oxygen), the seed absorbs water, swells, and the radicle (root) emerges first, followed by the shoot (stem).
3. Seedling:
- The young plant (seedling) grows, developing roots, stems, and leaves, and begins photosynthesis.
4. Mature Plant:
- As the plant grows, it reaches maturity with fully developed roots, stems, leaves, and flowers.
5. Flowering:
- The mature plant produces flowers, which contain the reproductive organs (stamens and pistils).
6. Pollination:
- Pollination occurs when pollen from the male organ (stamen) reaches the female organ (pistil) of the flower, often with the help of wind, insects, or animals.
7. Fertilization:
- The pollen fertilizes the ovule in the pistil, forming a zygote. This results in the development of seeds.
8. Seed Formation:
- Seeds develop within the ovary of the flower. The fertilized ovule becomes a seed, and the surrounding ovary becomes the fruit.
9. Seed Dispersal:
- Seeds are dispersed by wind, water, or animals to new locations, where they can germinate and start a new cycle.
10. Seed Dormancy:
- Some seeds enter dormancy, remaining inactive until conditions are suitable for germination.
This life cycle continues with the seeds growing into new plants, completing the cycle.