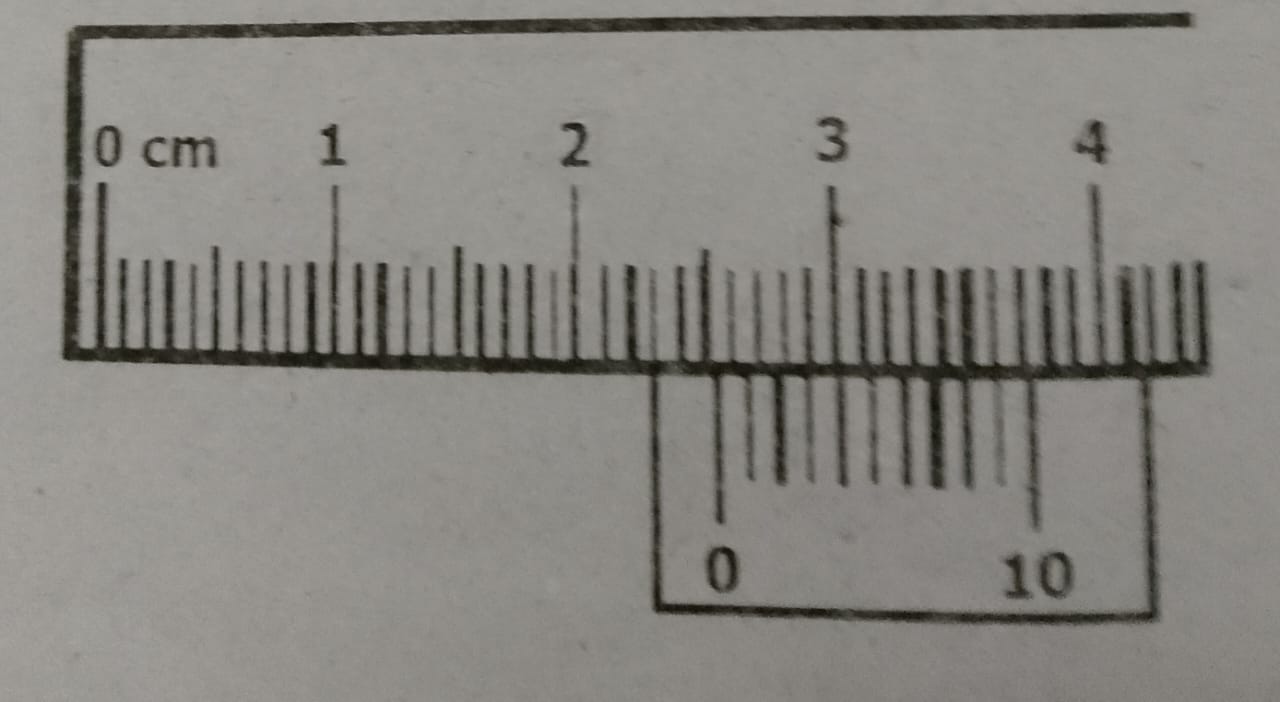
Q6. Look at the measurement of vernier calipers:
Look at the measurement of vernier calipers: a. What is its main scale reading? b. What is its coinciding division on the vernier scale? Calculate the total reading on the vernier calipers. Ans: a. The main scale reading (reading to which zero of vernier scale coincides) is 2.5 cm. … Read more