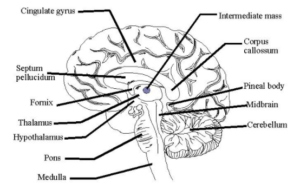
The human brain is a complex organ with multiple regions, each having distinct functions. It can be broadly divided into three main parts:
1. Cerebrum (Forebrain)
-
Largest part of the brain, responsible for higher cognitive functions such as thinking, reasoning, and memory.
-
Divided into two hemispheres: Left Hemisphere (dominant in language and logic) and Right Hemisphere (dominant in creativity, spatial awareness).
-
Cortex (Gray Matter): The outer layer of the cerebrum, responsible for voluntary actions, sensory perception, and complex cognitive tasks. The cortex is divided into lobes:
- Frontal Lobe: Involved in decision-making, motor control, and personality.
- Parietal Lobe: Handles sensory input, spatial orientation, and body awareness.
- Temporal Lobe: Important for processing auditory information and memory.
- Occipital Lobe: Responsible for vision processing.
-
White Matter: Beneath the cortex, consists of nerve fibers that transmit signals between different parts of the brain.
2. Cerebellum
- Located at the back of the brain, below the cerebrum.
- Coordinates motor control, balance, and posture.
- Plays a role in motor learning and fine-tuning voluntary movements.
3. Brainstem
- Connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls basic life functions such as heart rate, breathing, and sleep cycles.
- Composed of three main parts:
- Midbrain: Involved in visual and auditory processing, motor control.
- Pons: Relays signals between the cerebrum and cerebellum; involved in sleep regulation.
- Medulla Oblongata: Controls autonomic functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
Limbic System
- A set of structures involved in emotion, memory, and arousal:
- Amygdala: Emotion processing and memory formation.
- Hippocampus: Key for learning and memory.
- Thalamus: Relays sensory information to the appropriate areas of the brain.
- Hypothalamus: Regulates homeostasis, including hunger, thirst, and body temperature.
Other Structures
- Corpus Callosum: A bundle of nerve fibers connecting the left and right hemispheres of the cerebrum.
- Ventricles: Fluid-filled cavities in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions the brain.